Introduction
According to the IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Land (2019), global agriculture directly contributes approximately 8.5% of total greenhouse gas emissions, with an additional 14.5% resulting from land-use changes—mainly deforestation in developing countries to clear land for food production. Climate change exacerbates hunger and malnutrition by destroying crops, livelihoods, and self-sufficiency, creating a vicious cycle between agricultural production and climate impacts. Currently, around 1.9 million people face catastrophic hunger, and without immediate climate action, this crisis is likely to worsen.
Value
-
 EnvironmentalReduces GHG emissions and protects ecosystems.
EnvironmentalReduces GHG emissions and protects ecosystems. -
 EconomicImproves resource efficiency and mitigates regulatory risks.
EconomicImproves resource efficiency and mitigates regulatory risks. -
 SocialEnhances food security and strengthens public and investor trust.
SocialEnhances food security and strengthens public and investor trust. -
 Technological & IndustrialDrives green innovation and supports sustainable industry development.
Technological & IndustrialDrives green innovation and supports sustainable industry development.
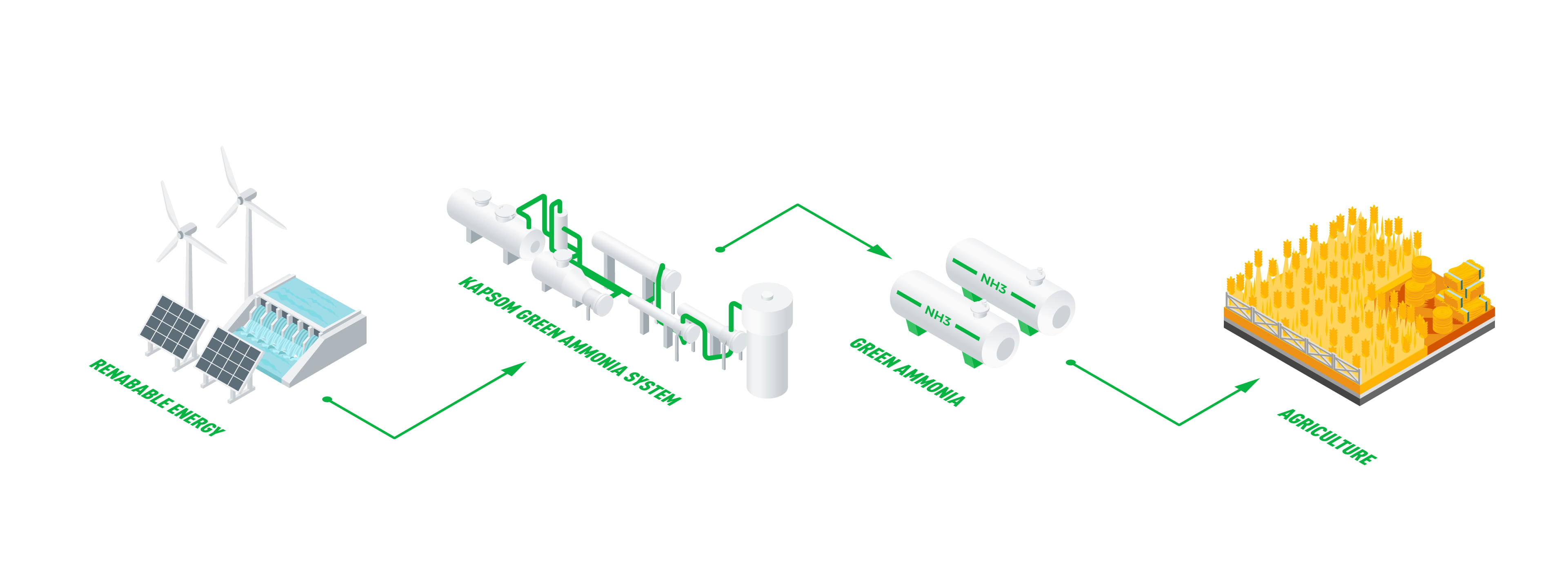
Illustration







 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported


